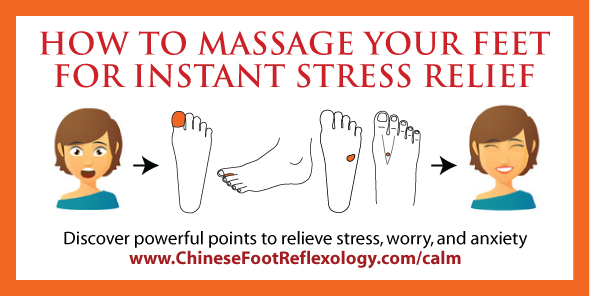
Atrial fibrillation - fibrillation of the muscles of the atria of the heart arrhythmia cardiac arrhythmia - an abnormal rate of muscle contractions in the heart fibrillation - muscular twitching involving individual muscle fibers acting without coordination. Atrial fibrillation or A-fib is a common type of arrhythmia or irregular rhythm.
 Apixaban Vs Warfarin In Patients With Atrial Fibrillation
Apixaban Vs Warfarin In Patients With Atrial Fibrillation
It is recognizable on an electrocardiogram by the absence of P waves and an irregular ventricular response.

Atrial fibrillation medical definition. An abnormal and irregular heart rhythm in which electrical signals are generated chaotically throughout the upper chambers atria of the heart. The heart beats too fast and its upper and lower chambers do not work together. Atrial Fibrillation also known as A Fib or AF is the most common arrhythmia abnormal heart beat where the heart beat is continuously irregular with no pattern to it at all.
Atrial fibrillation can decrease the hearts pumping ability. Such changes increase susceptibility to AF. AF increases the risk of stroke sixfold and is associated with a twofold increase in mortality which remains above 15-fold after adjusting for co-morbidity predominantly caused by cerebrovascular events.
The prevalence of atrial fibrillation AF already the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia is constantly rising even after adjusting for age and presence of structural heart disease. Definition of Atrial fibrillation. In addition atrial fibrillation that occurs over a long period of time can significantly weaken the heart and lead to heart failure.
Doctors need to determine which type of atrial fibrillation a. A cardiac arrhythmia whose basis is a disturbance in atrial activity. Atrial fibrillation also called AFib or AF is a quivering or irregular heartbeat arrhythmia that can lead to blood clots stroke heart failure and other heart-related complications.
The irregularity can make the heart work less efficiently. Atrial fibrillation AF risk factors RFs induce structural and histopathologic changes to the atrium that are characterized by fibrosis inflammation and cellular and molecular changes. Very rapid uncoordinated contractions of the atria of the heart resulting in a lack of synchronism between heartbeat and pulse beat abbreviation AFcalled also A-fib auricular fibrillation.
Atrial fibrillation a reentrant cardiac arrhythmia marked by rapid randomized contractions of the atrial myocardium causing a totally irregular rapid atrial rate. At least 27 million Americans are living with AFib. Atrial fibrillation AF is a common abnormal heart rhythm or arrhythmia.
Medical definition of atrial fibrillation. Persistent AF further induces electric and structural remodeling that promotes perpetuation of AF. Learn about symptoms risk.
An abnormal and irregular heart rhythm in which electrical signals are generated chaotically throughout the upper chambers atria of the heart. It is recognizable on an electrocardiogram by the absence of P waves and an irregular ventricular response. Atrial fibrillation is a type of arrhythmia or irregular heartbeat that often causes the heart to beat at an abnormally fast rate.
Persistent AFib is one of three main types of the. It causes your heart to beat abnormally which might feel like your heart is fluttering. Atrial fibrillation AFib is a type of heart disorder marked by an irregular or rapid heartbeat.
ˌeɪtriəl fɪbrɪˈleɪʃ ə n us ˌeɪtriəl ˌfɪbrəˈleɪʃ ə n abbreviation AF a problem in which the heart beats faster than normal and in a way that is not regular resulting in the atria the top spaces of the. Atrial fibrillation a reentrant cardiac arrhythmia marked by rapid randomized contractions of the atrial myocardium causing a totally irregular rapid atrial rate. Many people with atrial fibrillation have no symptoms.
Atrial fibrillation often occurs with heart defects cardiosclerosis rheumatic endocarditis and thyrotoxicosis but there is no generally accepted theory to explain how it develops. Many people with atrial fibrillation have no symptoms.
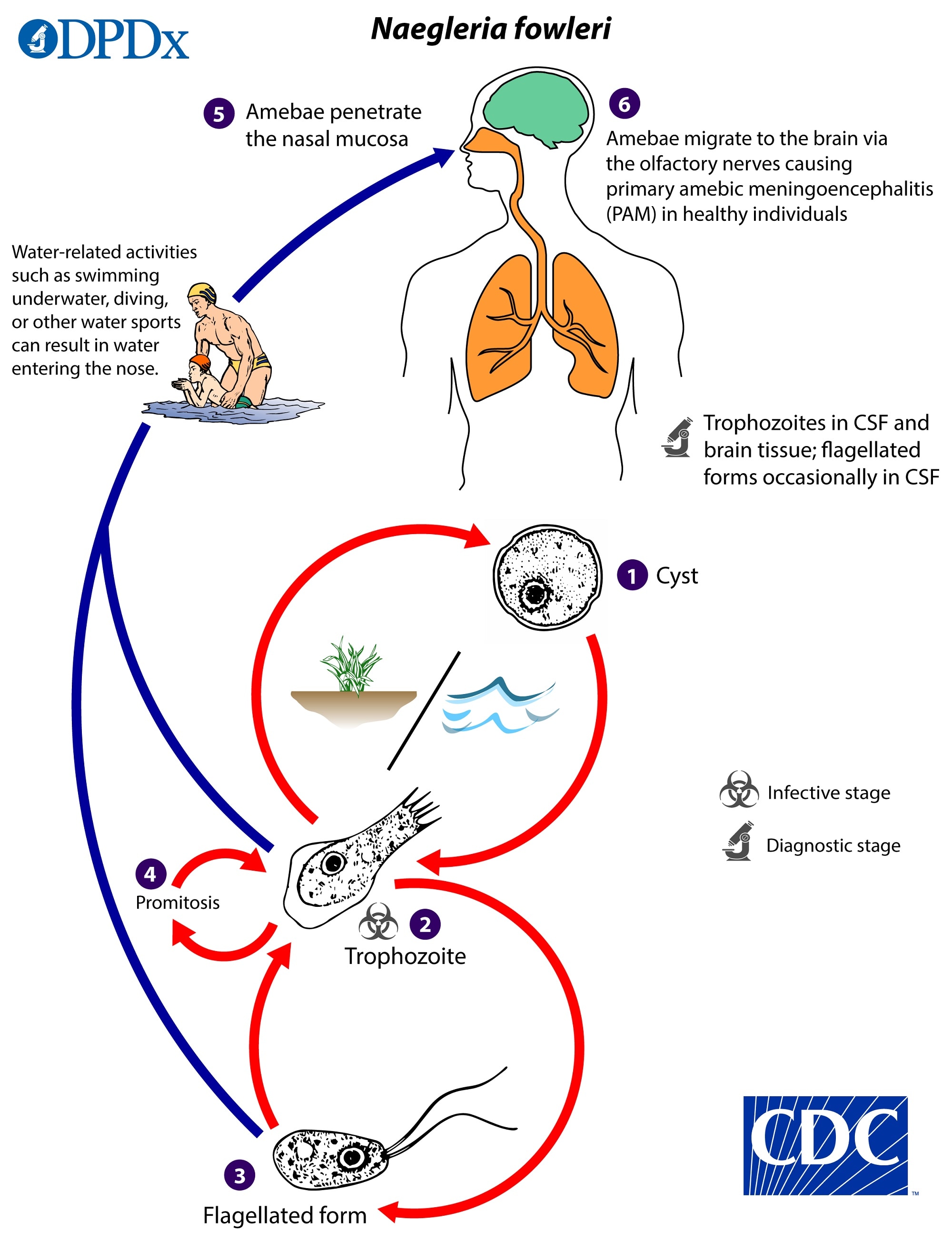







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/3145195-article-tips-to-reduce-stress-5a8c75818e1b6e0036533c47-922c3155e9c846eaa7447c75030b2c13.png)