In this immunity persons own cells produce antibodies in response to infection or vaccination. It is long lasting and is harmless.
 Acquired Immunity What Is It And How Do You Get It
Acquired Immunity What Is It And How Do You Get It
Active immunity is defined as immunity to a pathogen that occurs following exposure to said pathogen.
Active acquired immunity. Artificially acquired active immunity. Active immunity and passive immunity. Artificial active immunity and natural active immunity.
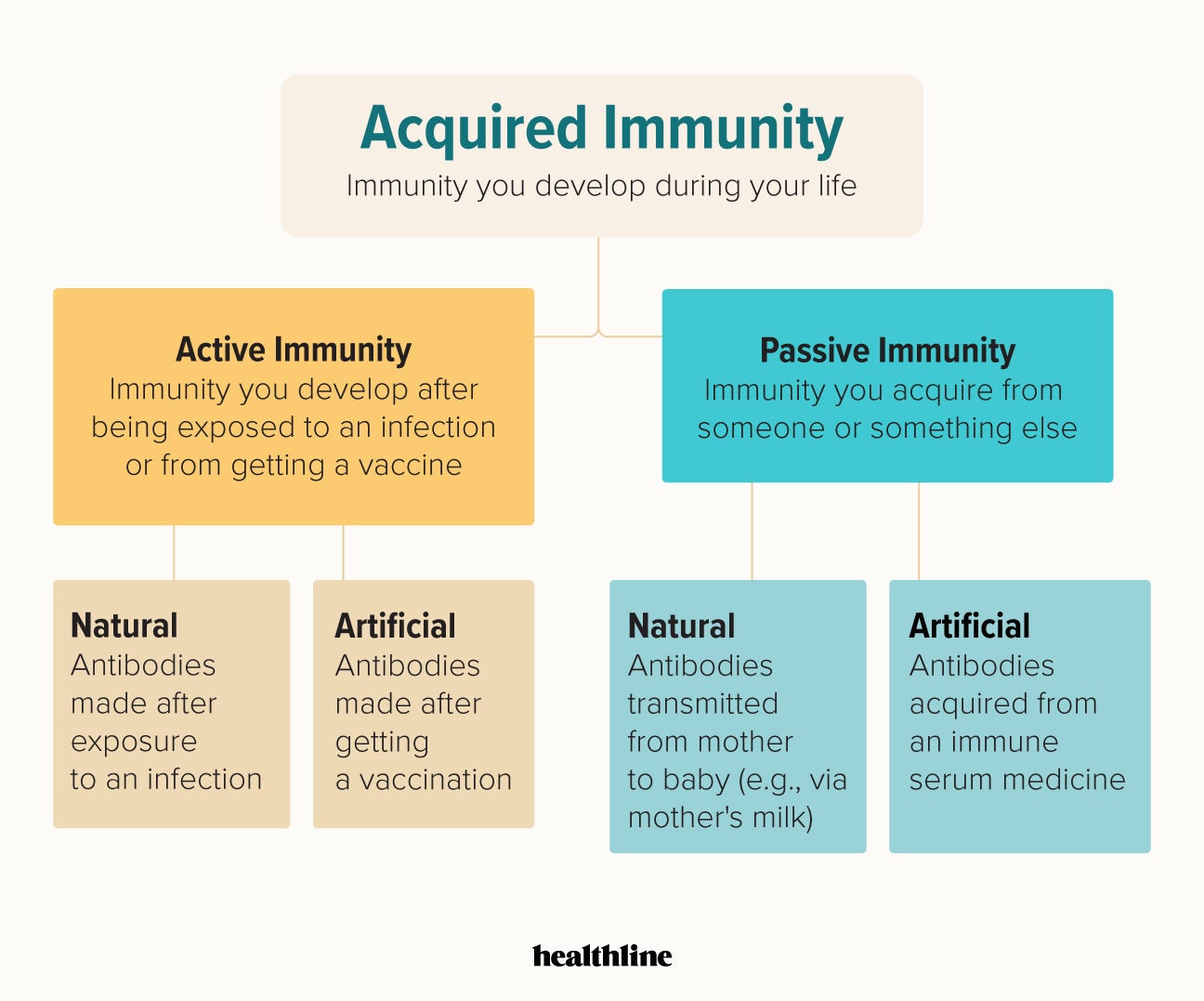
Immunity provided by vaccination. The two types of active immunity are naturally-acquired active immunity and artificially-acquired active immunity. Acquired immunity is immunity you develop over your lifetime.
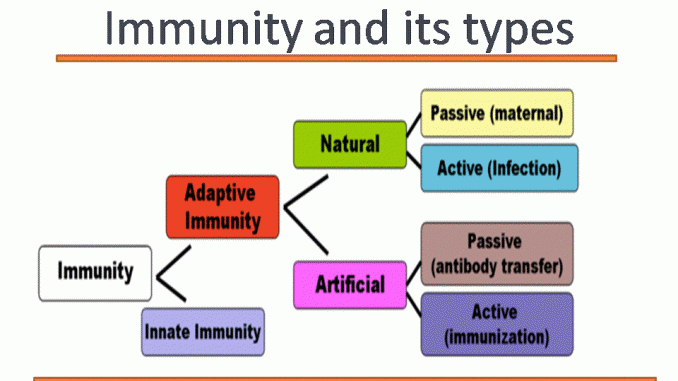
Acquired Adaptive Immunity is of two types. It relies on the body making antibodies which take time to mount an attack against bacteria or viruses. It is slow and takes time in the formation of antibodies.
Active immunity is the type of immunity acquired when one is exposed to a pathogen and the body actively engages in combating the pathogen as in a primary infection briefly explained above. It is of two types. Active immunity is the immune response to a pathogen.
Active immunity and passive immunity. Immunity can be described as either passive or active depending on how it is acquired. Immunity that develops during a persons lifetime.
Active naturally acquired immunity refers to the natural exposure to an infectious agent or other antigen by the body. The body responds by making its own. The primary immune response provides active immunity.
Types of acquired immunity. Active immunity results when exposure to a disease organism triggers the immune system to produce antibodies to that disease. Belongs to this kind of immunity only.
Passive immunity occurs when antibodies are introduced rather than made eg from breast milk or antisera. This type of immunity is usually obtained through vaccination or through administration of toxoids. If host itself produces antibodies it is called active immunity.
This is the means by which active immunity is acquired The artificial means by which one receives active immunization would be via vaccinations. It can come from a vaccine exposure to an infection or disease or from another persons antibodies. Immunity acquired through vaccines for various infectious diseases such as cholera tuberculosis plague pneumonia smallpox polio tetanus influenza measles rabies yellow fever etc.
Active immunity may be natural or artificial. Since the vaccinated individuals immune system is involved in the development of immunity it is referred as artificial acquired active immunity. By giving a safe form of the antigen artificially the body will produce its own antibodies and more importantly develop circulating long-lived B-memory cells with high affinity B.
Active Artificially Acquired Immunity Active artificially acquired immunity refers to any immunization with an antigen. Active immunity is acquired through continuing subclinical infections caused by bacteria and viruses which largely remain unnoticed and which is more advantageous than passive immunity. What is Active Immunity Active immunity refers to an immunity which results from the production of antibodies by the persons own immune system in response to a direct contact of an antigen.
A A person who has recovered from an attack of small pox or measles or mumps develops natural active immunity. Active immunity is due to the production of antibodies by the organism itself after the bodys defence mechanisms are stimulated by antigens. When the body is exposed to a novel disease agent B cells a type of white blood cell create antibodies that assist in destroying or neutralizing the disease agent.
There are two types of acquired immunity. The immune response occurs immediately.
