The CDC has standardized guidelines to help diagnose diarrhea a potential indicator of c. These institutional guidelines were updated in 2017 to reflect further.
 What Cdc Is Doing To Reduce C Diff Infections Cdc
What Cdc Is Doing To Reduce C Diff Infections Cdc
Its estimated to cause almost half a million infections in the United States each year.
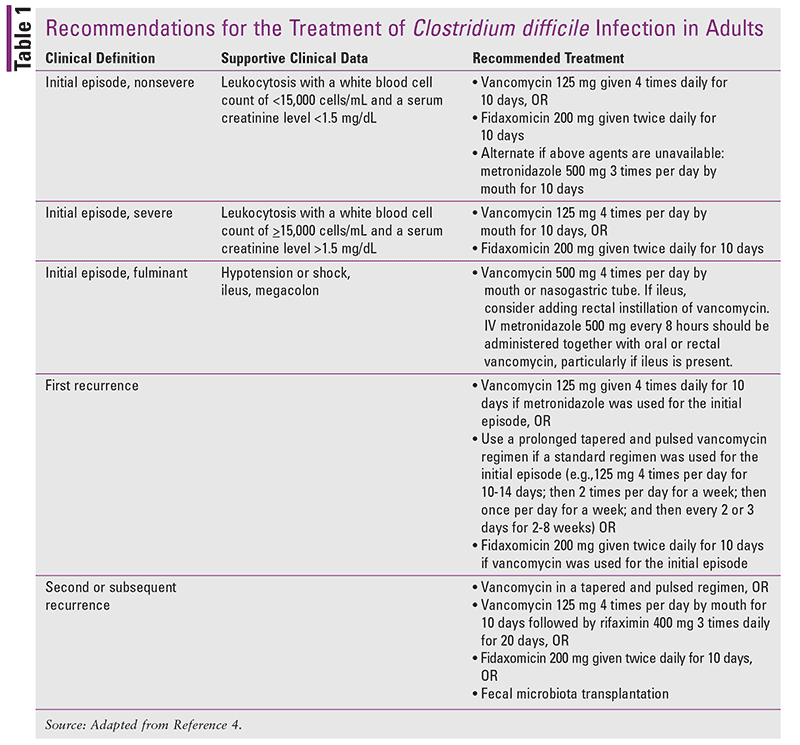
C diff guidelines cdc. Communicable Disease Management Protocol Clostridioides difficile Infection February 2019 5 and 5-7 among elderly residents in long term care facilities 1. Diff prevention such as environmental disinfection glove usage and anti-microbial stewardship but they dont take a firm stand on hand hygiene. Diff infection occur while youre taking antibiotics or not long after youve finished taking antibiotics.
Diff reassess correctness of antibiotics. Diff to themselves and to other patients. For two step testing methods order C.
Clinical Practice Guidelines for C. A gram positive bacteria that can form spores and produce toxins known as toxins A and B. Strategies to Prevent Clostridium difficile Infections in.
Difficile infection and colonization and treatment of asymptomatic colonization is not recommended. Only test acute diarrhea of unknown cause due to risk of false positive test. If order is pending ï hours and no diarrhea discuss canceling order with physician.
2017 Update by the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America SHEA and the Infectious Diseases Society of America IDSA Other relevant CDC guidelines. Resistant infections The Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America advises discontinuing contact precautions after obtaining between one and three negative cultures in certain cases of drug-resistant infections among other recommendations. Diff and handwashing might not be sufficient alone.
GUIDELINES FOR TREATMENT OF CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE COLITIS IN ADULTS Prior studies show that 3-26 of hospitalized patients are asymptomatically colonized with C. When should a toddler or older child be tested for C. Difficile Testing Guidance IMPORTANT Test POA present on admission diarrhea by day ï if C.
Wear gloves and gowns when treating patients with C. Poor antibiotic prescribing practices put patients at risk for C. New guidelines issued on contact precautions for C.
Toxin-producing strains may cause C. More than half of all hospitalized patients might get an antibiotic at some point during their hospital stay but studies have shown that 30 to 50 of antibiotics prescribed in hospitals are unnecessary or incorrect. Prescribe and use antibiotics carefully.
If youre in the hospital wash your hands with soap and water every time you use the bathroom and always before you eat. While caring for you and other patients with C. Diff is a germ bacterium that causes severe diarrhea and colitis an inflammation of the colon.
Diff infection CDI which can be severe and even fatal. Difficile Infection in Adults. Diff also known as Clostridioides difficile or C.
Difficile testing should not be routinely performed in children with diarrhea who are 12 years of age unless other infectious or noninfectious causes have been excluded weak recommendation low quality of evidence. Diff even during short visits. Isolate patients with C.
Strategies to Prevent C. CDI is associated with altering or eliminating the normal lower. Guidelines for the treatment of.
2017 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America IDSA and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America SHEA external icon. Diff immediately even if you only suspect CDI. Available assays are not able to distinguish between C.
Unnecessarily isolating individuals due to suspected c. Metronidazole is no longer recommended as first-line therapy for adults. Most cases of C.
Gloves are important because hand sanitizer doesnt kill C. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Clostridium difficile Infection in Adults and Children. Difficile toxin A appear to provide protection against CDI.
In patient being evaluated for C. Oral vancomycin and fidaxomicin are now recommended. Infection CDI were first produced by the Stanford Division of Infectious Diseases and Geographic Medicine in 2015 based in large part on the 2010 IDSASHEA guidelines.
Difficile Infection in Acute Care Facilities CDC 2018. Guideline updates released in 2018 reflect notable changes in treatment of C difficile infection CDI. Clostridioides difficile klosTRIDeOY-dees difuhSEEL is formerly known as Clostridium difficile and often called C.
Difficile and high levels of serum antibody against C. The CDC outlines a number of precautions for preventing the spread Cdiff including contact precautions proper sanitation and frequent handwashing. Difficile is a germ bacterium that causes severe diarrhea and colitis an inflammation of the colon.
The new CDC guidelines do a great job of covering some of the better-studied aspects of C. About 1 in 6 patients who get C. It can be found as part of normal flora.
Difficile infection CDI can place a financial burden on the healthcare system as well as cause emotional toil for the patient. Diff will get it. Diff can be life-threatening.
This is understandable because most of the data looking specifically at hand hygiene and C. Diff doctors nurses and other healthcare providers will use certain precautions such as gowns and gloves to prevent the spread of C. Hospitals that have experienced recent outbreaks will need to evaluate whether all of these precautions are being properly followed especially those related to sanitation and hand hygiene.
