Signs and symptoms of Marfan syndrome may include. Marfan syndrome is a connective-tissue disease inherited in an autosomal dominant manner and caused mainly by mutations in the gene FBN1.
 Marfan Syndrome Diagnosis By Prof Julie De Backer Youtube
Marfan Syndrome Diagnosis By Prof Julie De Backer Youtube
Treatment is based on which organs and body systems are affected.

Marfan syndrome diagnosis. Marfan syndrome is a genetic disorder with considerable morbidity and mortality. Relevant family history specific musculoskeletal abnormalities ocular lens subluxation and aortic dilationdissection. A child with Marfan syndrome is closely watched with physical exams and regular testing.
The essential simplified criteria for diagnosis are 3 out of the 4 following findings. Marfan syndrome can be difficult to diagnose because the signs and symptoms can vary from person to person. The heart eyes blood vessels and skeleton are most often affected by Marfan syndrome.
The child inherits from their parents. Connective tissue functions as a means to provide support strength and elasticity to various vital parts of body as tendons heart valves blood vessels cartilage and eyes. A parent with the illness inherits the abnormal gene from many people with Marfan syndrome.
A dissecting aorta can be a medical emergency. So far only a few studies based on older diagnostic criteria have reported a wide range of prevalence and incidence. A detailed medical and family history including information about any family member who may have the condition or who had an early unexplained heart-related death.
The clinical diagnosis is made using the. There are a number of criteria that your GP or geneticist a gene specialist will measure your. It is a condition that affects the connective tissue of body.
A diagnosis of Marfan syndrome is based on signs family history and results of diagnostic tests. This gene encodes fibrillin-1 a glycoprotein that is the main constituent of the microfibrils of the extracellular matrix. Most mutations are unique and affect a single amino acid of the protein.
This can be caused by the lens in one or both eyes moving out of place which is often the first sign of Marfan syndrome. Marfan syndrome MFS is a spectrum of disorders caused by a heritable genetic defect of connective tissue that has an autosomal dominant mode of. The most serious signs and symptoms associated with Marfan syndrome involve the cardiovascular system.
Marfan Syndrome Causes Reasons For Marfan syndrome encircle a gene defect that causes the entire body to make a protein which tends to provide power and elasticity to connective tissues. A chest that sinks in or sticks out. Marfan syndrome the fibres that support and anchor the organs and other components in the body is a hereditary condition that affects connective tissue.
What is Marfan syndrome Marfan syndrome also known as Marfans syndrome is a disorder that affects the connective tissue in many parts of your body. Marfan syndrome is a multisystem connective tissue disorder usually associated with mutation in fibrillin and occasionally with mutation in TGF BR1 or 2. Eye problems including blurred vision or trouble seeing things that are far away.
In most cases a diagnosis will be based on a thorough physical examination and a detailed assessment of a persons medical and family history. The diagnosis of Marfan syndrome relies on a set of defined clinical criteria the Ghent nosology developed to facilitate accurate recognition of the syndrome and improve patient management and counselingTo decrease the risk of premature or missed diagnosis an international panel of experts revised the criteria in 2010. A tall thin build.
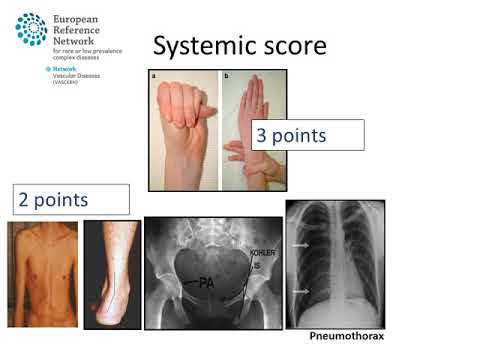
A long head with deep-set eyes. Skin striae dural ectasia hernias pneumothorax and emphysematous bullae on CXR may also be noted. Undue fatigue shortness of breath heart palpitations racing heartbeats or chest pain radiating to the back shoulder or arm.
Presently clinicians use the 2010 revised Ghent nosology which includes optional genetic sequencing of the FBN1 gene to diagnose patients. A Marfan diagnosis can often be made after exams of several parts of the body by doctors experienced with connective tissue conditions including. The differential diagnosis of a tall young person with Marfan-like skeletal features includes homocystinuria MIM 236300 Beals syndrome MIM 121050 MarshallStickler syndrome.
Cold arms hands and feet can also be linked to MFS because of inadequate circulation. Connective tissue provides strength and flexibility to structures such as bones ligaments muscles blood vessels skin lungs and heart valves. Marfan syndrome is one of the genetic disorders ie.
